Joins and More in SQL
Read other lessons from Kanchana here.
What is a Join?
Join is used for retrieving data from multiple tables .Using SELECT statements data is retrieved from two or more tables using a join clause. There are different types of joins. We will see two of them in this article.
For the examples discussed in this article we use the tables CUSTOMERS and TRANSACTION .Their table designs are as given.
CUSTOMERS
| Customer_no |
| Cust_name |
| Mid_name |
| Last_Name |
| Street Name |
| City |
| Pincode |
Transaction
| Transaction_no |
| Customer_no |
| Amount |
| Desc |
| Time Stamp |
| Balance |
1.INNER JOIN
SELECT customers.Customer_no, customers. Cust_Name, transaction.Transaction_no FROM customers
INNER JOIN transaction
on customers.Customer_no = transaction.Customer_no ;
The above statement retrieves all records from customers and transaction table where there exists a customer no in customers table that matches the customer no in transaction table.
Given below is the sample records for Customers and Transaction tables where only specific fields of concern are listed.
| Customer _no | Cust_name |
| C101 | Perry |
| C102 | Beiber |
| C103 | Swift |
| C104 | Byonce |
| C105 | Lady |
Transaction Table
| Transaction No | Customer_no | Time_stamp |
| T125437 | C102 | 01/01/2013 |
| T678975 | C103 | 09/01/2013 |
| T999567 | C105 | 12/09/2013 |
When the Inner Join query is executed we get an output as given below.
| Customer_no | Transaction_no | Customer Name |
| C102 | T125437 | Beiber |
| C103 | T67895 | Swift |
| C105 | T999567 | Lady |
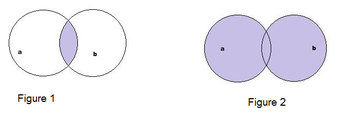
The representation in terms of visual diagrams would be as in Figure 1 above
Where a represents CUSTOMERS table and b represents TRANSACTION table. We get only those records which fall in the intersection of the circles as the output of the inner join.
2.FULL OUTER JOIN
A full outer join will return all the rows from both the tables. When the join condition is not met NULLS will be returned for those fields in the result set.
FULL OUTER JOIN transactionSELECT customers. Customer_no, customers.Cust_Name,transaction.Time_stamp FROM customers
on customers.Customer_no = transaction.Customer_no ;
The Sample Output
| Cust_no | Cust_name | Time Stamp |
| C101 | Perry | XXX |
| C102 | Beiber | 01/01/2015 |
| C103 | Swift | 09/01/2015 |
| C104 | Byonce | XXX |
| C105 | Lady | 12/09/2014 |
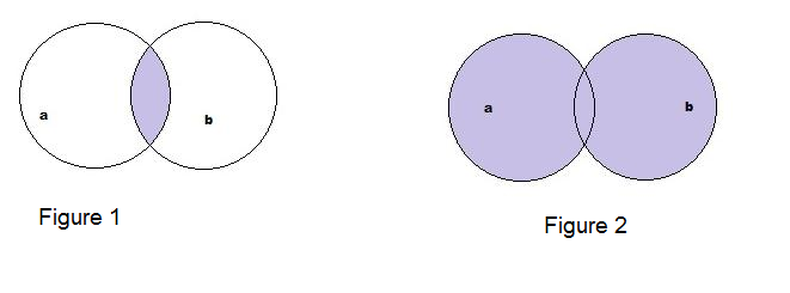
The representation in terms of visual diagrams would be like in Figure 2 above
Where a represents CUSTOMERS table and b represents TRANSACTION table. As seen the records listed are from both the circles completely.